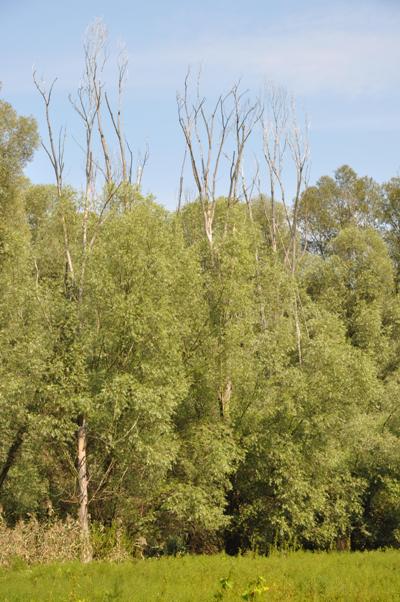
During the period 1977 to 1992 the construction of water dam (WD) Gabcíkovo was carried out. The technical implementation caused fall of groundwater levels, which consequently put floodplain forest ecosystems into risk. A hydro-technical project has been implemented to ensure regulatory groundwater regime based on the biological needs of the floodplain ecosystems. State of these ecosystems has been regularly observed in the framework of Complex monitoring of the WDs environmental impacts since 1992 when WD Gabcíkovo was launched into operation. Data and methods of remote sensing has been used for evaluation of floodplain forests state since 1992. Firstly, infrared aerial images were used, but multispectral ones have been exploited since 2008. Despite the fact that it is an effective method for forest state monitoring, its deficiency is that it does not allow assessing interior structure and quantitative characteristics of a forest stand. This is particularly important when assessing status and development of indigenous forest communities, especially softwood floodplain forests. Recent development in the field of remote sensing addresses this deficiency by exploitation of 3-dimensional methods of data collecting and interpretation. The progressive technologies include methods such as digital photogrammetry and airborne laser scanning (LIDAR). However, their application is limited due to lack of technical and software infrastructure and underdeveloped 3-D data processing methodologies. Due to complexity of the problem, it is necessary to address the issues in cooperation. This cooperation is based on the use of existing know-how (Monitoring of the Danube: ERTI Sárvár, NLC Zvolen; methodological aspects of Lidar data processing: NYME Sopron) and new LIDAR equipment (NLC Zvolen). Through the outlined cooperation between university (basic) and applied research, we expect to generate new methodologies using 3-D data in described forestry applications as well as cost-effective solution for the data processing.
Project title
Inovatívne metódy inventarizácie a monitoringu luných lesov Dunaja s vyuitím 3-D technológií dialkového prieskumu Zeme / Innovatív módszerek a Dunamenti ártéri erdok leltározására és monitorozására korszeru 3-D-s távérzékelési technológiák segítségével
Project title in English: Innovative methods for monitoring and inventory of Danube floodplain forests based on 3D technologies of remote sensing)
Project code
HUSK/1101/1.2.1/0141
Project duration
Project duration: 24 months
Start date: September 1, 2012
End date: December 31, 2014
Approved project budget of the partners
| Partner |
ERDF contribution |
State budget contribution |
Total |
National Forest Centre
(Lead partner) |
269 285,10 |
85% |
47 520,90 |
15% |
316 806,00 |
Hungarian Forest Research Institute
(Cross-border partner) |
91 188,85 |
85% |
16 092,15 |
15% |
107 281,00 |
University of West Hungary
(Partner 2) |
77 446,90 |
85% |
13 667,10 |
15% |
91 114,00 |
| TOTAL in EUR |
437 920,85 |
|
77 280,15 |
|
515 201,00 |
Geographical location of the activities
| Field work |
Office work |
Slovakia:
floodplain forests in the Danube inundation area, between the old river bed and the channel - field work related to data collection - dendrometric measurement in research plots and model locations will be carried out here as well as aerial photography
Hungary:
floodplain forests on the Hungarian side of the Danube, between the Danube and the dike, the area between Györ and Mosonmagyaróvár
|
Slovakia:
NLCs buildings at T.G. Masaryka 22 and Sokolská 2 in Zvolen
Note: the project team also includes staff members from branch offices in ilina (1 person) and Gabcíkovo (1 person)
Hungary:
ERTI Budapesti Ksérleti Állomás, 1027 Bp. Frankel L. út 1. (HU101)
Nyugfat-magyarországi Egyetem Sopron, Bajcsy-Zs. Út 4. Pf. 132
|